Top 10 Solar Project Solution Factory In China
Working mode1
Self-use (with photovoltaic power)
Energy flow priority: Load > Battery > Grid
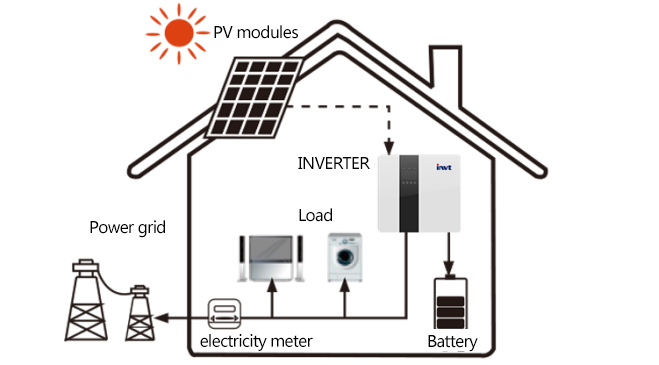
1.This mode is applicable to areas with low grid-connected electricity price and high energy price. The electricity generated by the photovoltaics will first be used to power local loads and then to charge batteries, with excess power being exported to the public grid.
2.When the light is insufficient, the solar power is not enough to meet the household load power. At this point, the battery discharges and meets the household load with solar power, or if the battery is low, the power is supplied from the grid.
3.When the light is good and the battery is fully charged, the solar modules supply power to the household load and feed the surplus energy to the grid.
1.From the economic point of view, this mode greatly reduces the purchase amount of power grid electricity price, improves the photovoltaic application rate, and reduces the cost of household energy use. It is suitable for household light storage scenarios with large electricity consumption and large difference in stepped electricity price.
2.From the point of view of power grid, the overlap of photovoltaic power generation and load energy use in the daytime is high, which conforms to the duck curve theory. The increase in the proportion of local utilization of new energy greatly reduces the photovoltaic power grid and reduces the osmotic pressure of local distribution network.
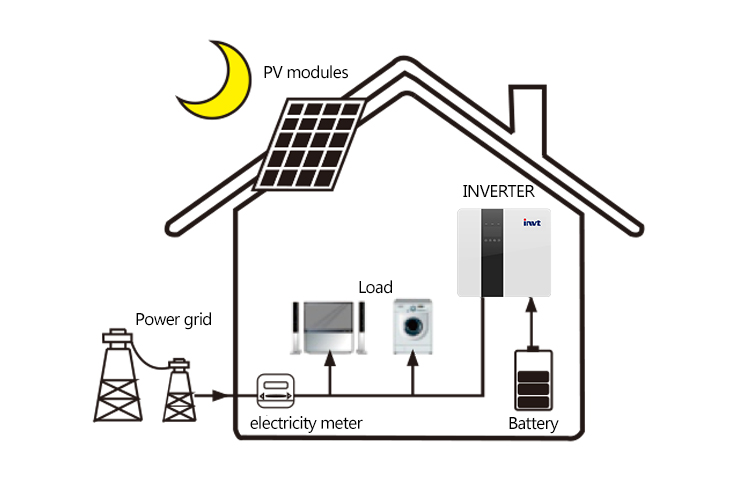
When there is no PV supply, the battery will discharges from the load, and when the battery capacity is low, the grid supplies power.
Working mode2
Energy flow priority: Battery > Load > grid (when charging)
Priority: Load >Battery>Grid (when discharging)
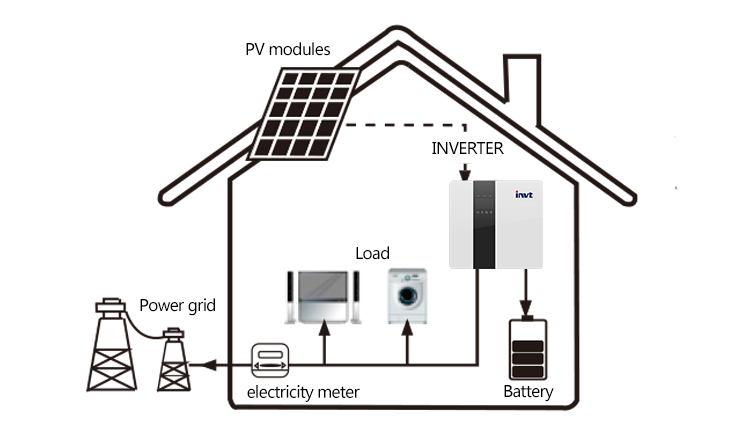
Application Scenario: This mode is applicable to areas with peak valley electricity price (TOU). Users can use photovoltaic power, off-peak power, to charge the battery. Charging and discharging time ranges can be set flexibly, and you can choose whether or not to charge from the grid.
Advantages: This model can set the charging and discharging time of the machine reasonably according to the time of time-of-use electricity price in the installation area. It stores electricity when prices are low and releases it to feed the load when prices are high. Essentially, it is a profit model of peak-valley .
Working mode 3:Standby Mode
Energy flow priority: Battery > Load > grid

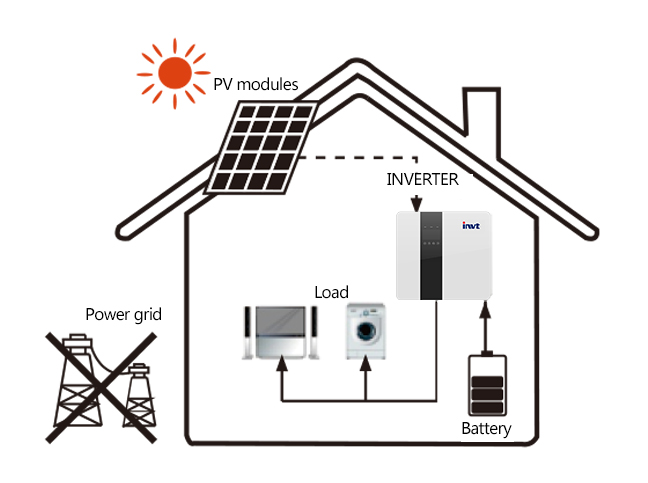
This mode is applicable to areas with power outages frequently. This mode ensures that the battery has enough power to supply when the grid is disconnected.
In this mode, the battery will be forced to charge for a set period of time and never discharge when the grid is connected. It also allows to choose whether or not to charge from the grid. In standby mode, there are three scenarios:
Scenario 1: Rigid Demand
For example, in regions without electricity in Tibet, it is difficult to supply power to large power grids due to the population is relatively dispersed, large investment in long-distance transmission, and poor power quality. For example, in Africa, South America and Southeast Asia, the quality of power grids is not high and unstable, the power supply is insufficient, and the power facilities are relatively backward, which further increases the demand for backup power in these regions.
Scenario 2: Emergency power supply (equal to UPS power supply function)
When the grid shuts down, the system will provide emergency power via photovoltaic or battery to power the household loads.
1.Frequent natural disasters lead to power grid blackout( eg: In coastal areas, typhoons, earthquakes, wildfires and other natural disasters are relatively frequent, and the power supply is forced to suspend.)
2.Power supply for important equipment: Level-1 or extra level load, namely, equipment that cannot be powered off or cannot be powered off for a long time, such as oxygen supply equipment, monitoring equipment, communication data processing equipment, financial and public security system, etc. The importance lies in the fact that once the power supply of these devices is insufficient or poor, it may lead to major accidents such as property damage or personal safety.
Scenario 3: Powered for independent system
Off-grid photovoltaic + energy storage system is generally applied to some areas that cannot be covered by the power grid, such as some remote mountain residents, border defense, guard posts, islands, mobile monitoring stations, offshore ships and other areas or scenes that are not suitable for access to the power grid.
